Cloud Computing for Financial Services: Benefits and Challenges
The financial services industry, from banking and insurance to investment management, is undergoing a massive digital transformation. Driven by customer expectations for seamless, personalized experiences, the need for agility, and the ever-present pressure to reduce costs, financial institutions are increasingly turning to cloud computing. This shift promises to revolutionize how these organizations operate, innovate, and serve their customers. However, the highly regulated and sensitive nature of financial data means that cloud adoption isn’t without its challenges.
Cloud computing offers financial services companies the opportunity to leverage scalable infrastructure, advanced analytics, and innovative technologies without the significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance associated with traditional on-premises systems. This allows them to respond more quickly to market changes, develop new products and services faster, and ultimately gain a competitive edge. But navigating the complex landscape of cloud security, regulatory compliance, and data governance is crucial for a successful transition.
This article delves into the benefits and challenges of cloud computing for the financial services sector. We’ll explore how cloud technology can address key industry pain points, examine the potential risks and security concerns, and discuss the strategies that financial institutions can employ to ensure a secure and compliant cloud migration. From enhancing customer experience to streamlining operations, understanding the nuances of cloud adoption is essential for financial services companies looking to thrive in the digital age.
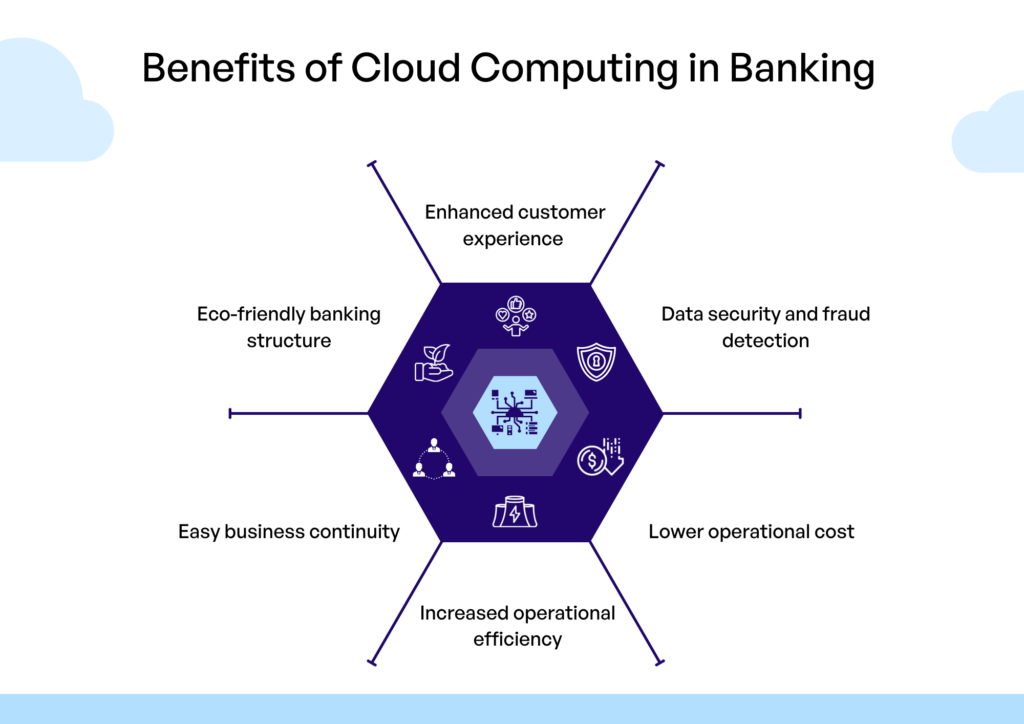
Benefits of Cloud Computing for Financial Services
The financial services industry stands to gain significantly from embracing cloud computing. Here are some of the key benefits:
Enhanced Agility and Scalability
Traditional on-premises infrastructure often struggles to keep pace with the dynamic demands of the financial market. Cloud computing provides the agility and scalability needed to quickly adapt to changing market conditions, launch new products and services, and handle fluctuating transaction volumes. Financial institutions can easily scale their resources up or down as needed, paying only for what they use, which eliminates the need for over-provisioning and reduces capital expenditure.
Improved Customer Experience
Cloud-based solutions enable financial institutions to deliver personalized and seamless customer experiences across multiple channels. By leveraging cloud-based analytics and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, they can gain deeper insights into customer behavior, tailor products and services to individual needs, and provide more efficient and responsive customer support. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
Cost Optimization
Migrating to the cloud can significantly reduce IT infrastructure costs. Cloud providers handle the maintenance, upgrades, and security of the underlying infrastructure, freeing up internal IT resources to focus on more strategic initiatives. The pay-as-you-go model of cloud computing also eliminates the need for large upfront investments in hardware and software, leading to substantial cost savings over time.
Faster Innovation
Cloud platforms provide access to a wide range of innovative technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics. These technologies can be used to automate processes, detect fraud, personalize customer interactions, and develop new financial products and services. By leveraging the cloud, financial institutions can accelerate their innovation cycles and stay ahead of the competition.
Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud-based collaboration tools enable teams to work together more effectively, regardless of their location. This is particularly important for financial institutions with geographically dispersed operations. Cloud platforms provide secure and centralized access to data and applications, facilitating seamless collaboration and knowledge sharing among employees.
Improved Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities. Cloud providers typically have multiple data centers located in different geographic regions, ensuring that data and applications remain available even in the event of a natural disaster or other unforeseen disruption. This helps financial institutions minimize downtime and maintain business operations in the face of adversity.
Challenges of Cloud Computing for Financial Services
While the benefits of cloud computing are compelling, financial institutions must also address several challenges to ensure a successful and secure cloud migration:
Security Concerns
Security is paramount in the financial services industry. Financial institutions handle highly sensitive data, including customer account information, transaction details, and personal identification information. Migrating this data to the cloud raises concerns about data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance with data privacy regulations. Financial institutions must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems, to protect their data in the cloud.
Regulatory Compliance
The financial services industry is subject to strict regulatory requirements, such as the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Financial institutions must ensure that their cloud deployments comply with these regulations. This requires careful planning, documentation, and ongoing monitoring to demonstrate compliance to regulators.
Data Governance
Data governance is the process of establishing policies and procedures for managing data assets. In the cloud, data governance becomes even more critical. Financial institutions must define clear data ownership, access controls, and data retention policies to ensure data quality, integrity, and compliance. They also need to implement data loss prevention (DLP) measures to prevent sensitive data from leaving the cloud environment.
Vendor Lock-in
Vendor lock-in is the risk of becoming dependent on a single cloud provider. This can limit flexibility and increase costs in the long run. Financial institutions should carefully evaluate their cloud provider options and consider using open-source technologies and multi-cloud strategies to avoid vendor lock-in.
Integration Complexity
Integrating cloud-based systems with existing on-premises infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming. Financial institutions may need to re-architect their applications and data to ensure seamless integration. They should also consider using integration platforms as a service (iPaaS) to simplify the integration process.
Lack of Skilled Resources
Cloud computing requires specialized skills and expertise. Financial institutions may face a shortage of skilled resources to manage their cloud deployments. They should invest in training and development to upskill their existing IT staff or consider hiring cloud experts to help them with their cloud migration.
Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty refers to the legal requirement that certain types of data must be stored and processed within a specific country or region. Financial institutions must ensure that their cloud deployments comply with data sovereignty regulations. This may require them to choose cloud providers with data centers located in the required geographic regions.
Strategies for Successful Cloud Adoption in Financial Services
To overcome the challenges and maximize the benefits of cloud computing, financial institutions should adopt a strategic and well-planned approach to cloud adoption:
Develop a Cloud Strategy
A well-defined cloud strategy is essential for a successful cloud migration. The strategy should outline the organization’s cloud goals, objectives, and priorities. It should also address key considerations such as security, compliance, data governance, and vendor selection.
Assess Security and Compliance Requirements
Financial institutions must carefully assess their security and compliance requirements before migrating to the cloud. They should identify the relevant regulations and standards and implement appropriate security controls to ensure compliance. This may involve conducting risk assessments, implementing security policies, and obtaining third-party certifications.
Choose the Right Cloud Model
There are several cloud deployment models to choose from, including public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Financial institutions should carefully evaluate their options and choose the model that best meets their needs. Public cloud offers the greatest scalability and cost savings, while private cloud provides greater control and security. Hybrid cloud combines the benefits of both public and private cloud. For more information, you can refer to What is the cloud? as an additional resource.
Implement Strong Security Controls
Strong security controls are essential for protecting sensitive data in the cloud. Financial institutions should implement measures such as encryption, access controls, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention (DLP) to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Establish Data Governance Policies
Clear data governance policies are crucial for ensuring data quality, integrity, and compliance in the cloud. Financial institutions should define data ownership, access controls, and data retention policies. They should also implement data quality monitoring and data lineage tracking to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
Monitor and Manage Cloud Resources
Continuous monitoring and management of cloud resources are essential for ensuring optimal performance, security, and cost efficiency. Financial institutions should implement cloud monitoring tools to track resource utilization, identify potential security threats, and optimize cloud spending.
Train and Educate Employees
Cloud computing requires specialized skills and expertise. Financial institutions should invest in training and education to upskill their existing IT staff and ensure that they have the knowledge and skills needed to manage their cloud deployments.
Start Small and Iterate
A phased approach to cloud migration is often the most effective. Financial institutions should start with smaller, less critical workloads and gradually migrate more complex applications and data to the cloud. This allows them to learn from their experiences and refine their cloud strategy along the way.
Conclusion
Cloud computing offers significant benefits to the financial services industry, enabling enhanced agility, improved customer experience, cost optimization, and faster innovation. However, financial institutions must address the challenges of security, compliance, data governance, and vendor lock-in to ensure a successful and secure cloud migration. By developing a well-defined cloud strategy, implementing strong security controls, establishing data governance policies, and investing in skilled resources, financial institutions can unlock the full potential of cloud computing and thrive in the digital age. The key is to approach cloud adoption strategically, prioritizing security and compliance at every step, and continuously monitoring and optimizing their cloud deployments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the adoption of cloud computing within the financial services industry presents a compelling, yet complex, proposition. As we’ve explored, the potential benefits, including enhanced scalability, reduced operational costs, and improved data analytics capabilities, are substantial and offer a significant competitive advantage. However, these advantages must be carefully weighed against the inherent challenges of security, regulatory compliance, and the complexities of integrating cloud solutions with existing legacy systems. Navigating this landscape requires a strategic and informed approach.
Ultimately, the successful integration of cloud technologies hinges on a thorough understanding of the specific needs and risk tolerance of each financial institution. By prioritizing robust security measures, proactively addressing regulatory requirements, and embracing a phased migration strategy, firms can effectively harness the power of the cloud. As the financial services sector continues to evolve, embracing innovation while mitigating risks will be crucial for sustained success. We encourage financial institutions to further investigate and explore the possibilities of cloud computing, ensuring they are well-positioned to thrive in the rapidly changing digital landscape. For more in-depth information on secure cloud implementation strategies, please visit our dedicated cloud security resource page.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Cloud Computing for Financial Services: Benefits and Challenges
What are the primary benefits of using cloud computing for financial services institutions, particularly regarding cost savings and scalability?
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages to financial services institutions. A significant benefit is cost reduction. By migrating to the cloud, firms reduce capital expenditure on hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure maintenance. They shift to an operational expenditure model, paying only for the resources they consume. This leads to substantial savings, especially for smaller institutions. Another key advantage is scalability. Cloud platforms allow financial institutions to easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak periods and avoiding over-provisioning during quieter times. This flexibility is crucial for adapting to market fluctuations and new business opportunities. Moreover, cloud solutions often provide enhanced disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities, increasing resilience and reducing downtime.
What are the key security challenges and compliance considerations financial institutions face when adopting cloud computing solutions, and how can they be mitigated?
Adopting cloud computing presents specific security challenges and compliance considerations for financial institutions. Data security is paramount, requiring robust encryption, access controls, and threat detection mechanisms to protect sensitive financial data from breaches. Compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific standards (e.g., PCI DSS) is crucial. Mitigation strategies include selecting cloud providers with strong security certifications, implementing comprehensive data governance policies, conducting regular security audits and penetration testing, and utilizing data loss prevention (DLP) tools. It’s also vital to establish clear roles and responsibilities for data security and compliance between the financial institution and the cloud provider. Thorough due diligence is crucial when choosing a cloud provider, ensuring they meet the stringent security and regulatory requirements of the financial services sector.
How does cloud computing enable innovation and improve customer experience in the financial services industry, and what are some examples of innovative cloud-based applications?
Cloud computing fosters innovation and enhances customer experience in financial services by providing a flexible and scalable platform for developing and deploying new applications. Cloud-based solutions enable faster time-to-market for new products and services, allowing institutions to respond quickly to changing customer needs. Examples of innovative cloud-based applications include: AI-powered fraud detection systems that analyze transactions in real-time, personalized financial planning tools that leverage data analytics to provide tailored advice, and mobile banking platforms that offer seamless and convenient access to financial services. Cloud computing also facilitates the use of big data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences, leading to more targeted marketing campaigns and improved customer service. The agility and scalability of the cloud empower financial institutions to experiment with new technologies and deliver more engaging and personalized customer experiences.